Agriculture remains a cornerstone and backbone of Ghana’s economy, employing a significant portion of the population and contributing substantially to Gross Domestic Product (GDP). GDP represents the total monetary value of all goods and services produced within a country’s borders in a specific time period, typically measured annually or quarterly. It is a key indicator used to assess the economic health of a nation. However, traditional farming methods often limit productivity and sustainability. The integration of technology into agriculture presents transformative opportunities to enhance efficiency, productivity, and food security.

Key Technologies Transforming Agriculture
Mobile Technology and Apps: Information Dissemination Mobile apps provide farmers with timely information on weather forecasts, pest control, and market prices. This empowers them to make informed decisions.
Market Access: Platforms like Esoko connect farmers directly to buyers, reducing intermediaries and increasing profit margins

Precision Agriculture
Data Analytics: Technologies such as GPS and drones allow for precision farming, enabling farmers to monitor crop health, soil conditions, and resource usage more effectively
Resource Optimization: This approach helps in optimizing water usage and fertilizer application, leading to cost savings and higher yields.
Irrigation Technologies
Drip and Sprinkler Systems: Modern irrigation systems are essential for enhancing water use efficiency, especially in areas vulnerable to drought. These systems help maintain consistent crop growth and reduce water waste.
Biotechnology
Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs): The development of drought-resistant and pest-resistant crops has the potential to increase yields and ensure food security amid climate change challenges.
Biofortification: Enhancing the nutritional content of staple crops addresses malnutrition while improving agricultural productivity


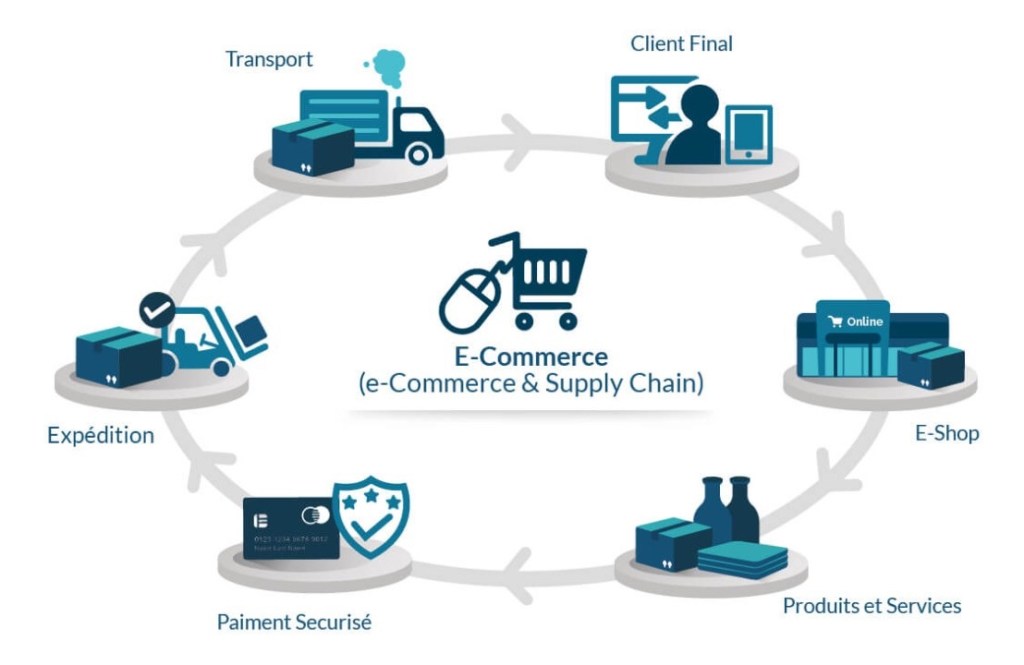
E-commerce and Supply Chain Innovations
Online Marketplaces: Platforms like Farmerline facilitate the sale of agricultural products, enabling farmers to reach broader markets and improve income stability.
Supply Chain Management: Technology streamlines logistics, ensuring timely delivery of inputs and products, which is vital for maintaining quality and freshness.
Benefits of Technological Integration
- Increased Productivity: Enhanced farming practices lead to higher yields and more efficient resource use.
- Economic Growth: By improving the agricultural sector, technology contributes to broader economic growth and poverty alleviation.
- Food Security: Technology helps ensure a stable food supply, essential for the growing population and urbanization.
- Sustainability: Technological advancements promote sustainable practices, such as reduced pesticide use and improved soil management.
Government and Institutional Support
The Ghanaian government, alongside NGOs and international organizations, plays a crucial role in promoting agricultural technology. Initiatives include:
- Investment in Research and Development: Supporting agricultural research institutions to innovate and adapt technology to local needs.
- Subsidies and Financial Support: Providing subsidies for technology adoption and access to credit facilities for farmers.
- Training Programs: Implementing capacity-building programs to educate farmers about modern agricultural practices and technologies.
Conclusion
The integration of technology in Ghanaian agriculture offers a pathway to enhanced productivity, economic growth, and sustainability. While challenges remain, targeted support from the government and stakeholders can facilitate the widespread adoption of these technologies, ultimately transforming the agricultural landscape and improving the livelihoods of farmers across the country.